Oral Hygiene during the Pandemic: Role of Complimentary Oral Hygiene Methods
The pandemic opened up a debate on preventive oral care. Preventive dental care is of utmost importance in such situations and may even help us fight against the virus and our overall health. Let us go through some of the measures and the oral care materials that can help us keep our teeth and general mouth health intact even during times of staying long periods at home.
Some of these measures require a trip to the dental office, but it can be a worthwhile effort for a long-term protective action on teeth.
Brushing Times: Day or Night?
Is brushing at night more important than brushing in the morning?
Have you wondered whether it makes sense for you to not brush your teeth at bedtime? You might have told yourself that since you brush in the morning, your teeth are protected. However, there could not be a more damaging habit to teeth than not brushing at night.
Brushing at night is more important than brushing at any other time. This is not to say that brushing in the morning is not important enough. It just means that brushing at night is a little more important. We will tell you why.
During the day, our teeth are protected by the neutralizing action of saliva, which is not the case while we sleep. To understand the importance of proper brushing at night, you need to understand how dental decay develops.
Root Cause of Dental Decay
Bacteria acts on food debris trapped between teeth, producing lactic acid. It is this acid that removes minerals from tooth (de-mineralization), causing cavities.
Stages of Dental Decay
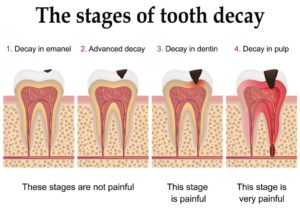
Stage 1: Demineralization
Enamel is the outermost layer of our teeth and is the hardest tissue matter in our body. Enamel is composed of minerals. As teeth are exposed to lactic acid produced by bacteria, the enamel begins to lose these minerals. At this stage, you might see white spots appearing on teeth, which is a sign of demineralization and cavity formation.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay
The next stage of demineralization is cavitation, where the white spots progress further to form brown spots that develop into caries or cavities. At this stage, brushing or remineralizing cannot help your teeth and a dentist will have to fill up the cavity.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay
Once the cavities are allowed to continue without intervention from the dentist, the dentin, that is the next layer after the enamel and softer than the enamel, begins to get affected. The dentin has nerve endings that may present itself as sensitivity to hot and cold food.
Stage 4: Pulp Damage
Once the damage reaches the pulp which is the innermost layer of teeth, there will be response from the body defence mechanism in the form of swelling, that cannot be accommodated by the surrounding tissue, and hence puts pressure on the nerves, leading to pain.
Stage 5: Abscess Formation
Abscess formation is the final stage of a dental decay, with the infection leading to a pocket of pus at the base of the tooth causing intense pain spreading to your neck, jaws, and facial regions. Here the option is to clear the infection, desensitizing the tooth by removing the nerves and filling up the canals using cement. The tooth in some cases may even have to be removed.
Here lies the importance of brushing twice a day to remove trapped food particles, with the onus being on brushing at night. During daytime, lactic acid produced by bacteria is neutralized by active ingredients in saliva. When we sleep at night, saliva production is considerably less or close to nil as the body does not require it for digestion of food, or lubrication of mouth during speech. This leads to protection from saliva being close to nil when we sleep. Thus, the importance of proper mouth cleaning before sleep. This can only be achieved through proper brushing before bedtime.
However, it is important to know that brushing alone cannot remove food trapped between teeth?
There are certain inaccessible areas inside the mouth that the toothbrush cannot easily reach, such as the areas between teeth and the back portion of teeth. Food gets easily trapped in such places. To remove the stuck food debris, we need other types of cleaning devices such as the Dental floss, Water-floss or Waterpik and Interdental brushes that can pull out or flush out debris from inaccessible areas.
Regular use of the above-mentioned devices is required to completely eliminate the remnants of food caught in-between teeth and not removable through brushing.
Dental Floss

A dental floss is a chord or thin chord-like material used to remove food debris stuck between teeth. The use of the dental floss is recommended highly in addition to toothbrushing every day and helps in the removal of gingivitis and plaque.
How to use Dental Floss
Break off 18-24 inches of the floss from its casing by pulling it and twirling it on your fingers. Use the rest of the portion (around 1-2 inches) part of the material to remove the food stuck between your teeth using delicate up and down motion. The flossing movement should not cut the gums, so movement should be against the sides of the teeth.
Use of Tooth Mousse & its Role in Preventing or Delaying Cavities
GC Tooth mousse is the miracle solution formulated by the scientists of the University of Melbourne, Australia. It is basically Calcium Phosphopeptide, derived from the milk protein Casein. When casein encounters free calcium and phosphate released during demineralization process, they form a stable compound called amorphous calcium phosphate which is acid-resistant, and hence powerful enough to stop/ prevent tooth decay.
Application of Tooth Mousse
The ideal time to apply tooth mousse is just before bedtime. This is because during daytime, saliva washes away applied tooth mousse, thus exposing the teeth to the risk of decay.
How to Apply GC Tooth Mousse
It is amazingly simple to apply tooth mousse. Just before bedtime, after regular tooth brushing, apply a pea sized amount of tooth mousse to teeth. You can apply on each tooth using a cotton ball or clean fingers. Repeat for all teeth and then go to bed. You need not wash this off when you get up in the morning.
The Role of Fluoride Varnish in Preventing Dental Decay

Fluorides are present in most of the available commercial tooth products including toothpastes. However, the time of contact that the fluoride content in such products has with teeth is not enough to allow the formation of a protective shield/ barrier, rendering them ineffective, whereas fluoride varnishes have more contact time with teeth.
When fluoride comes into contact with teeth, forms Fluorapatite crystals. These fluorapatite crystals are resistant to bacterial acid attack, preventing tooth decay. The time that the fluoride remains in contact with teeth is critical for crystal formation. Toothpaste with fluorides do not remain in contact with the teeth surface for a long time, and hence are not effective in preventing decay through the formation of crystals.
Application
Application of the varnish is best done by a qualified dentist, even if one can do it at home, with the efficacy of application not as good as the former. At the dentist’s office, the application would be more professionally carried out.
Method of Application at the Dentist’s Office
After properly isolating teeth, fluoride varnish is applied on tooth surfaces. Once applied, teeth should remain without contact with water or food for 4 hours to allow the formation of protective fluorapatite crystals.
Interdental Brush

Another way of preventing dental decay is to use the interdental brush for cleaning the area between the gums and the teeth. An interdental brush has soft bristles that can bend to fit in between the space of the gums and teeth. It can also be used to clean the area between orthodontic brackets and the teeth.
Mouth bacteria build a coating that we call biofilm on teeth surfaces; this biofilm is actually a layer of living organisms strung together using reinforcing elements. It is here that the bacteria thrives, multiplying and breeding in a more protected environment. Basically, biofilm is like bacteria building villages, towns, and cities – but on our teeth. When bacteria breed in the safety of the biofilm, they produce a lot of waste. The bigger and stronger the biofilm, the more waste bacteria produce. This waste offsets the chemical balance on our teeth, and leads to tooth decay, bad breath, and gum disease. When the film is too thick and strong, we call it dental plaque. Naturally, we want to avoid plaque as much as we can. (*Content courtesy: Gently from Curaden)
How to destroy Plaque
The only way to properly destroy the biofilm is physically disrupting its structure through brushing. This removes a lot of the biofilm and saves the tooth from decay. However, an interdental brush augments this process through removal of stubborn food particles stuck between the gums and the space between the teeth.
The interdental brush has a flexible head with bristles that can bend and get inside the space between the gums and teeth, and this can physically remove biofilms built by bacteria. Interdental spaces are inaccessible pretty much by toothbrushes and accessible by interdental brush heads.
How to use Interdental Brushes
As mentioned, insert the flexible head of the gum pick or the interdental brush between the space between the gums and the teeth and move it up and down to remove the food matter stuck there. When you are undergoing orthodontic treatment, use the same methodology to clean the space between the brackets and the teeth structure. The brush has to be then cleaned in running water. Because of the bristles, ID brushes are more effective in cleaning food debris than even flossing.
You might experience temporary bleeding when first using an interdental brush for the first time: this is a sign that a mild form of gum disease has already started near the interdental space, and by brushing you have disrupted a small portion of the gum that contains tiny blood vessels. It is a good thing you caught it early, because a little later you could be getting the same kind of bleeding from conventional brushing. Do not worry; once you clean out the biofilm from in between your teeth, the gum inflammation will go away, the blood vessels will be protected and there will be no bleeding. (*Source: Curaden’s Gently Blog)
Conclusion
The pandemic situation made it essential for all of us to take care of our oral health seriously than before. For non-critical issues related to the teeth, preventive measures can help keep us safe at home even when similar situations arise. Even otherwise, oral health is a door to overall physical health and mandates preventive measures to keep us fit and fine.
For more details on the preventive measures mentioned above and to order the above materials, please reach out to us on +91 8943109396 or write to us at hanumatagenciestvm@gmail.com




Leave a Reply